|
At Food Fur Life, we advocate for and encourage the feeding of raw food. That said, a (properly balanced) home prepared food made with all human grade ingredients, even if cooked, will always – in our opinion – be a superior choice to any commercial canned or kibble. This is why we formulated EZComplete fur Cats to properly balance food whether the meat used with the premix is cooked or raw. The premix powder includes both pancreas and digestive enzymes so all kitties fed food made with our premix are consuming those needed digestive enzymes. We understand there may be personal reasons to cook. With that in mind, we share the information in this article to help you make informed choices: whether or not to cook, and if cooking, which method will both suit your lifestyle and be most healthful for your kitty.
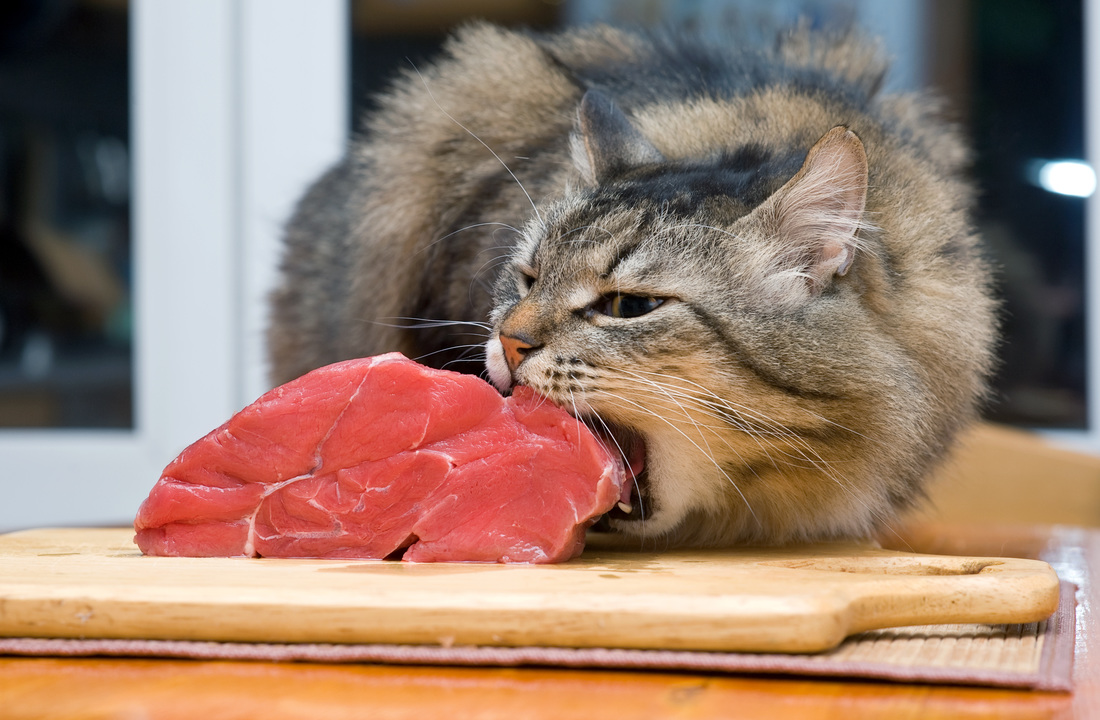
When we first entertain the idea of homemade food for our pets, it’s quite common to have questions, if not concerns, about raw feeding and bacteria. Unless we are lucky enough to have a veterinarian that is knowledgeable about raw feeding, these questions often grow into fears once we chat about the diet change (if the notion of homemade food is not completely discouraged). The only consideration when it comes to cooking for our pets, typically, is the fear-based potential for bacterial contamination. We treat the question "to cook or not to cook?" as if cooking is benign, and has no impact apart from making food “safer.” Sure, we all know we need to account for nutrient loss. But the decision to cook for our pets is not so straightforward. There are other important factors to consider – especially if it is cancer or an inflammatory disease that prompted us to explore making food for our furry family members. Having eaten cooked food for anywhere from 400,000 to 1.8 million years, humans have adapted to eating cooked food. Our pets, naturally hunters and scavengers, have not. In their evolutionary timeline, commercial foods only became a part of their diet full time within the last few decades. Cooking their food may have unintended health consequences, as they are perfectly designed for eating not just raw meat and organ, but what we would consider contaminated raw meat and organ. Of course WE would likely get sick if we ate raw meat contaminated with bacteria. But this an instance where we should not humanize our pets. Veterinarians are quick – and rightly so – to point out the nutritional needs of our pets are quite different than our own. Of course those differences extend to the defense systems of our bodies versus those of our pets. Of course our pets are well adapted to their natural evolutionary diets of hunting and scavenging. And of course our pets have biological mechanisms in place to protect them from this risk that we do not. We address this in our article “Why You SHOULD Feed Your Immune Compromised Cat Raw Food.” So what is the real difference between raw and cooked? Cooking:
Why are enzymes so important to our pets? Enzymes are present in all living animal (and plant) cells: they are the catalysts of all naturally occurring biochemical processes that take place in our (and our pets’) bodies. Without enzymes, we cannot utilize the nutrition we eat, and neither can our pets. The processes that enzymes catalyze would take so long without them, we couldn’t survive. As we have discussed in numerous articles, cats are not “just” carnivores, cats are metabolically inflexible hypercarnivores. Biologically, cats have made no adaptations to eating anything other than their natural diet. And that diet is raw. As Dr. Jean Hofve explains in the Spring 2012 issue of IVC Journal in her article, “Enzymes,” “The thousands of enzymes produced by the body aid in a wide variety of chemical reactions. There are two major classes of enzymes: metabolic and digestive. Digestive enzymes are produced primarily in the pancreas and released into the duodenum to help digest food coming from the stomach. The intestines themselves also secrete amylase and other digestive enzymes.” Dr. Hofve goes on to note that “Research in animals has shown that the production of digestive enzymes is independent of diet. That is, animals are biologically programmed to produce specific types and amounts of digestive enzymes in response to food ingestion, regardless of what food they actually eat. Only major evolutionary shifts, such as changing from omnivorous to insectivorous lifestyles, affect these systems. Our carnivorous pets have not, and cannot, adapt their digestive functions to processed diets, which, after all, have only been widely used for a few decades.” [Bold, our emphasis] In the wild, cats eat the entire animal. Their digestive and metabolic systems are designed to benefit from the supplemental enzymes consumed. When we feed our pets cooked food, we are providing food that is devoid enzymes. While cooking is a form of "predigestion" in that it alters the structure of the proteins in any food making it easier to break down, humans have had, as discussed above, at least four hundred thousand years to adapt to cooked food. So it is that our organs, especially our pancreas, are much larger relative to body size compared to that ratio in other animals. Dr. Hofve also addresses this in her IVC Journal article on enzymes for pets. The bottom line is that we have had hundreds of thousands of years to adapt to this change in food eating. It is only within the last 20 years or so that many cats were brought indoors 100% of the time, becoming 100% dependent on our cooked, literally processed to death foods, requiring long lists of vitamins and minerals be added back. We see the impact of this change to a diet lacking any fresh raw food or any hunted or scavenged prey in the top health issues and diseases cats suffer. As Dr. Hofve points out, “Evidence … strongly suggests that eating foods devoid of enzymes as a result of cooking, food irradiation, and microwaving causes an enlargement of the pancreas and also stresses associated endocrine glands… In all of nature, the human pancreas is three times larger, as compared to total body weight, than that of any other animal. What is interesting is that when mice are fed cooked foods, the ratio of their pancreas weight to total body weight becomes approximately that of a human’s. When they are switched back to a raw-food diet, their pancreas shrinks back to normal size. The most obvious conclusion is that the pancreas becomes hypertrophied, or enlarged, because it is forced to keep up a high digestive enzyme output.” [Bold, our emphasis] It would seem this process is happening to our cats. In a 2008 review article on pancreatitis by researchers at Texas A&M, it was noted that necropsy examination of the pancreas of 115 cats (both sick and healthy) discovered findings consistent with pancreatitis in 67% of cases (including 45% of “apparently healthy cats”). Let that sink in a moment. Two-thirds of cats had an enlarged pancreas consistent with chronic pancreatitis. We do not know that lack of enzymes in the diet is a cause of or even contributor to pancreatitis. But as the incidence of pancreatitis causing illness in our cats has risen to the point of ranking in the top 10 reasons for a vet visit in 2015 (according to Nationwide (formerly VPI) Pet Insurance), we should be mindful of their need for additional enzymes if eating cooked foods. It is a true testament to the resilience of our cats that so many do as well as they are, having had zero time in the scale of the species to adapt to any of the dietary changes we have forced them to make. The lack of enzymes is just one of many. Is cooked food ever appropriate for my pet? Older pets being transitioned to homemade, or pets with very damaged or sensitive GI tracts, may only be able to eat cooked food comfortably until their GI tracts have had time to heal. When your pet has a bout of diarrhea or vomiting, or if your pet has inflammatory bowel disease and/or pancreatitis and is in a flare, feeding a bland diet of plain cooked meat for a short period of time is often recommended to help settle the GI tract. Am I harming my cat if I feed cooked meat? There are no studies of the impact of Malliard reaction compounds or Advanced Glycation End products in cats. But if we suspect those compounds may present similar health problems to our cats as to ourselves, it is best to be mindful of the problem and make informed cooking choices. Low temperatures and moisture minimize AGEs and do not produce Maillard reaction compounds like heterocyclic amines. A slow cooker on low, the stove top in simmering water, or our baking instructions using moist heat (adding water to the pan and covering the pan with foil) are the best choices. With high heat, dry cooking (typically grilling, frying or roasting), the food will contain these compounds. Of course, as with everything, moderation is advised. You can provide your cat a tasty treat, but don't feed them something cooked via such high heat all the time. In addition to cooking at lower temperatures and with moisture, you can further minimize the impact of cooking by adjusting the "doneness" of the meat. If you are not convinced our pets are safe eating raw meat, consider lightly cooking the meat instead of cooking it to well done. The surface of the meat is the only area that may have been exposed to bacteria, so it is only the outside of the meat that needs to be cooked. There is no need to cook the meat all the way through. Importantly, this approach offers kitty the opportunity to benefit from some primarily raw food with most of its structure, nutrition, and enzymes intact.
0 Comments
Does your cat frustrate you with loving her food one day – and hating it the next? You might be surprised to learn that the problem could be the nutritional profile of the food you are offering her to eat, not the taste. Of course, cats experience nausea when ill. But a recent study indicates our apparently healthy kitties may have a sound reason for being finicky felines after all. “Balancing macronutrient intake in a mammalian carnivore: disentangling the influences of flavour and nutrition” found that – after a period of introduction to the food textures and flavors – aroma, taste and texture of food was not as important to cats as the macronutrient content of the food. “Macronutrient” content refers to the basic composition of the diet: protein, fats and carbohydrates. As we have discussed before, cats naturally consume a diet that is over 60% protein, about 20% fat, and has almost no carbohydrates (on a dry matter basis). As fat provides almost twice as many calories as protein, this equates to cats obtaining about 52% and 46% of their energy needs from protein and fat, respectively. (The diet they naturally consume provides just 2% of their energy from carbohydrates). In this study, cats were introduced to three basic new foods. These were wet foods with the texture of porridge. The flavors were fish, rabbit and orange. (!!!) Each food was initially formulated with a similar protein-to-fat ratio. The cats showed a strong preference for the fish-flavored food: rabbit was “neutral,” and orange flavored food disliked. No surprise there, right? The three different flavors of food were then formulated with three different ratios of protein and fat. On an energy basis, the three different food formulations were
When fed with those three different protein-to-fat options but offered just one flavor at a time, the protein-to-fat ratio of 70%/30% won as the favorite food, paws down. Then the cats were offered the varying protein-to-fat ratios with a mix of flavors such that the cats would have to eat orange flavored food in order to increase the protein in their diet. The cats ate a mix that averaged out to about 50% energy from protein and about 50% from fat, in line with the profile of their natural diet and the results of the 2011 study that eliminated taste preferences – even though that meant the cats had to choose to eat orange flavored food to achieve that mix of protein and fat. Adrien Hewson-Hughes, who led the study, told the Discovery News site, Seeker, “Cats initially selected food based on flavor preferences, but after 'learning' (due to prior exposure) about the nutritional composition of the foods, cats [subsequently] selected foods to reach a particular target balance of protein and fat regardless of added flavors.” Take a moment to absorb that. Cats chose a nutritional composition over taste and smell. As noted in the study discussion, “What is remarkable given the unusual nature and properties of the foods offered in these experiments — ‘porridge-like’ consistency, added flavours/aromas, different P : F [protein and fat] compositions and animal- or plant-derived protein sources — is the extent to which the balance and amounts of protein and fat intakes do converge... This indicates that macronutrient balancing is a powerful driver of food selection in cats and points to the ability to detect and respond to post-ingestive macronutrient signals that are distinct from sensory aspects contributing to the apparent palatability of foods.” (Our emphasis) In plain English, this means cats respond not just to taste, smell or texture – their bodies prompt them to eat what they need from a nutritional standpoint! It bears repeating: cats actually ate orange-flavored food (after learning it was, in fact, food) in order to consume a diet that (from the perspective of the ratio of meat and fat in the foods) resembles their evolutionary diet. As we have discussed before, cats are a metabolically inflexible hypercarnivore, and it really should come as no surprise that the diet they naturally strive to eat is what they need. It may be surprising to some that THEY know they need this. The mechanism responsible for this is not yet known. But what is most likely surprising to most (if not all) of us is the response of their bodies to diet is so strong, in order to get the nutrition they need, cats will eat food a food with a flavor they would most likely never – under normal circumstances – elect to eat on a taste/aroma basis. The qualifier there? They need to have been introduced to the foods and learn that they ARE food. Cats NEED to Be Introduced to New Foods If given the opportunity – and, importantly – when properly introduced to the food – cats will choose the diet that best suits their needs. As Dr. Hewson-Hughes told Discovery News, cats display an eating characteristic called neophobia. "This means they are unwilling to try a food that is new or different to their normal food, which may make them appear fussy." If we offer our kitty new food, especially a new food format such as wet from kibble or homemade from kibble or canned, we can’t expect them to like it right away – and we may meet with quite a bit of resistance. Cats are naturally cautious eaters and when a new food looks, smells, and feels so different, it is a part of their life-saving instinct to be distrustful. This is why we have several files dedicated to assisting with the process that results in a successful transition. Cats may instinctively know what they need – but most need to go through the learning process to understand that even healthy, tasty food IS food. Another interesting aspect of this study explains why cats, when they do take to a food if based just on taste, can so often appear to change their minds. This study indicates that every time you feed your cat, her body tells her whether she needs more or less of the nutrients in the food you’re offering her. If it has the same mid- or low-level of protein as what you were feeding; or if it has a similar carb content- she may well refuse the new food after a meal or two, despite liking the taste at first. So rather than commit to that new case of canned food, consider making your own cat food. A homemade balanced and complete cat food based on the prey model is what your cat needs – and your cat’s body knows it. With balanced and complete assurances (and the ability to use boneless raw or cooked meats) when you make your feline friend food with EZComplete fur Cats, you control the types AND cuts of meat you feed your cat. You control the mix of meat and fat. You control the texture (and temperature). If your cat doesn’t want ground food, you can feed it chunked. If your cat doesn't like gravy, add less water. Food Fur Life provides the tools you need to feed your cat the food her body wants and needs. **** 20% off EZComplete Fur Cats - Use Promo Code 20offnow at checkout ****
It's Healthy & Happy Cat Month! Feed your cat the way nature intended with EZComplete - Balanced homemade raw meals in one EZ Step. *Offer Expires on September 20th, 2016. Not Valid with any other offer. To keep up to date on Food Fur Life's News and Offers, please subscribe to our newsletter here.
You finally won the battle of wills with your cat, transitioned him to a raw diet, and all of the sudden you prepare his meal with a whole bunch of love and care only for him to sniff it and turn around – What a slap on your face you think! What happened? It’s the same food he was devouring yesterday!
Cats! You think… Raw food made my cat sick!... Hunger strike! You think... He’s Just super finicky, or he’s playing a game on me! Or he doesn’t like the food anymore… You are at a loss. There are several possibilities to consider when a cat stops eating, especially when transitioning to a raw diet: The first, and the most important thing to do is to rule out illness.
Prior to transitioning to a raw diet, most pet parents are accustomed to feeding their cats the same food meal after meal, sometimes for years, and their cats never get bored – so they naturally think it will be the same way with raw. It is no coincidence that kitty never gets tired of kibbles. Kibbles, and many canned foods are meticulously “engineered” to keep your kitties eating them, by being coated with fat, having chemicals and flavors added to it that are both irresistible and downright addictive. If that was not the case, pets would not eat processed foods. Transitioning your pet from kibbles or even canned to raw is the equivalent of transitioning an adult human, a lot of times even a senior citizen, who has only eaten highly processed foods from a can, package, or a bag his entire life to a healthy diet of salads, veggies, fruits and low fat meats. Not an easy task. It can take time, patience and perseverance…. But it’s absolutely the best thing you will ever do for your cat’s health, and a very rewarding experience for you too! Keeping in mind that the beginning can be difficult, and sometimes it will seem you are taking two steps back and one forward, always remember two key things: This is not a race, it’s a journey, and to never, EVER starve a kitty into a new diet. If kitty is not eating and you must take a step back in the transition, take a deep breath, take a step back, and move forward. There is nothing wrong with it – as long as you keep moving in the right direction and don’t give up, you will get there! With that said, now that you have taken that step, what can you do to keep your cats interested on raw? VARIETY. Variety is key in keeping your cats eating a raw diet long term. You should aim to have at least three proteins on your cats’ diet – that will provide them not only with a well-rounded nutritional profile, but will keep them from getting bored. Once you transition your cat to raw, immediately start using that protein as a base using the slow transition technique to add a second protein to the kitty’s diet. You can then use both proteins as a base to slowly introduce a third protein to the diet. When you have introduced all the proteins, you can switch them back and forth. How often should you rotate proteins? I personally rotate proteins at every meal – my cats never eat the same protein twice in a row. While EZComplete is considered almost a topper by most cats with the dried liver, GLM and yolk, variety is still essential in keeping my cats happy, and has yet to fail me in all these years. You can also rotate daily, or every few days, but in my experience the more often you rotate, the more successful you will be in keeping your cats anxious for the next meal, and licking their plates clean. Try a different texture - Many cats also get introduced to raw on ground meats, and stop eating... Then they are offed a chunk of meat and voila! That happened to our Food Fur Life Cats… Pretty much all of them! So if your cat is currently eating ground meat and no longer wants the food, try giving a little chunk of meat and see what happens. It might be time to take your kitchen scissors out of the drawer! Offer a plain meal - Also part of our variety, is once a week they get one or two completely plain meals – yep – no supplements, nothing! Meat only. That makes them love both the meat and EZComplete even more! Use healthy toppers - If you still have problems, and we all do from time to time, you can always rely on healthy toppers to entice your cat to eat. In my home, chicken is not a favorite for my cat Lucky, and I have to admit, she is a master manipulator (anyone here can relate to that?) – so from time to time I do rely on her favorite treat as a topper, which….. you guessed it – is Freeze Dried Chicken! I just lightly sprinkle it over her meal, and she licks her plate clean.
The Importance of a Routine
It’s also very important to note that cats are creatures of habit – that’s not a myth. Establishing a routine for them from the beginning is very important – from a feeding schedule, to their eating places, and even to their own plates. A set routine will impact your chances of success greatly. Before feeding raw, I had the hardest time to feed even half an ounce of wet food to any of my cats – I would have to crawl under the bed for one, spoon feed another on the top of the cat tree… Let alone the food had to be made into a slurry on a blender and warmed up just so, otherwise they would not even consider it! Think I am lying? Watch the video below of me spoon-feeding Bugsy! This was mainly due to two things - feeding kibbles along with wet, and having no routine.
One of the most valuable advice I have ever gotten, and I got MANY, was to establish a routine right off the bat when transitioning to raw – I believe that was essential for my cats being the happy carnivores they are today. I can easily see how important this is when anything breaks that routine – they go off food until their routine is back into place. If your cat suddenly quit eating, consider if anything has thrown his routine off.
Last, but not least, please consider your kitties’ situation when you transitioned them to raw. Lots of pet parents make that transition due to an illness, specially IBD… There is a reason why we recommend a slow transition – always. Especially on adult or older kitties, after years of eating an unappropriated diet, it can take time for their bodies to start digesting raw properly. EZComplete has both Enzymes and pancreas, which helps with digestion, but there are some kitties that make the transition with a digestive system already very compromised. These cats should be given an extra slow transition, always be on probiotics (we firmly believe probiotics are an essential part of the diet for all cats), and depending of the age or condition of the cat, they might have to start with a homemade cooked diet balanced with EZComplete, and slowly transitioned to raw. If you just transitioned to raw and feel your cat might have a tummy upset, your transition might have been be too fast. Take a step back, always follow your kitties pace, keeping a close eye on them. Summarizing, if your kitty suddenly stopped eating:
Most of you must recognize the word "Kefir" from the milk/yogurt aisles in the supermarket.... But do you know what Kefir is? The word Kefir derives from the Turkish word keyif, which means "Feeling Good" , and it's believed to be original from the Caucasus Mountains. Its history is full of legends, and can be "traced" all the way to the Prophet Mohamed and mentioned by Marco Polo! It is also believed Kefir was used as a way to preserve milk by means of fermentation, in the absence of refrigeration and pasteurization. Kefir grains were added to milk, generally in a goat skin leather bag, and hung by the door. Everyone who went by or through the door, shook the bag with its foot. After 24 hours, the fermented milk was poured, and fresh milk was added to the grains, keeping the fermentation process constant. 
But just what are the Milk Kefir Grains?
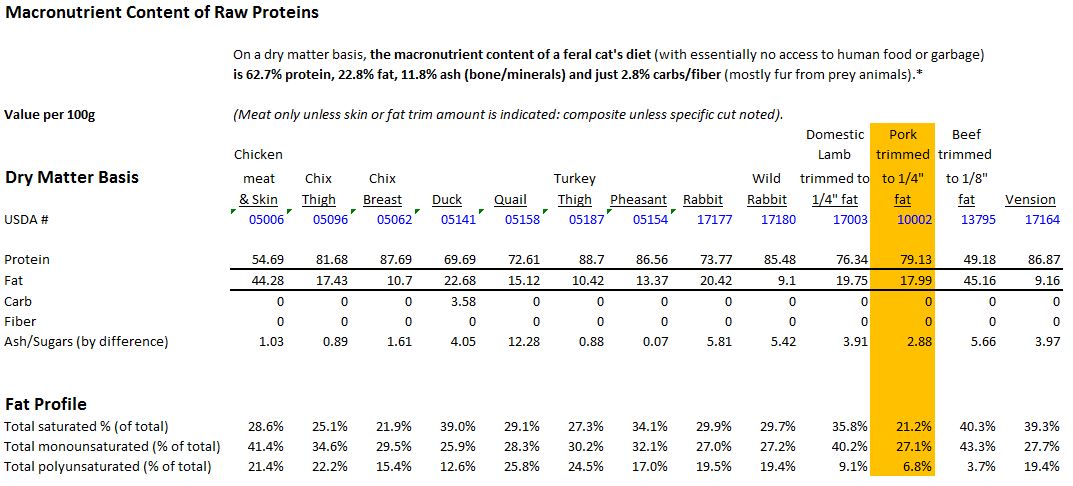
Kefir grains are microbially derived protein and polysaccharide matrices that contain cultures of bacteria and yeast that are essential to Kefir fermentation. The bacteria found in the grains depend of several factors, including the Milk used during fermentation, the fermentation process itself, and even the region where the grains originate from. Mainly comprised of Lactobacillus, common bacteria strains include: Ref 1, Ref 2, Ref3 Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus brevis, Lactobacillus casei, Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. delbrueckii, Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. lactis, Lactobacillus helveticus, Lactobacillus kefiranofaciens subsp. kefiranofaciens, Lactobacillus kefiri, Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. paracasei, Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus rhamnosus, Lactobacillus sake, Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris, Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis, Lactococcus lactis, Leuconostoc mesenteroides subsp. cremoris, Leuconostoc mesenteroides subsp. dextranicum, Leuconostoc mesenteroides subsp. mesenteroides Pseudomonas, Pseudomonas fluorescens, Pseudomonas putida, Streptococcus thermophilus Yeast Strains: Candida humilis, Candida Kefyr, Kazachstania unispora, Kazachstania exigua, Kluyveromyces siamensis, Kluyveromyces lactis, Kluyveromyces marxianus, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Saccharomyces martiniae, Saccharomyces unisporus, Debaryomyces hansenii, Dekkera anomala, Torulaspora delbrueckii, Pichia fermentans, Saccharomyces turicensis, Issatchenkia orientalis and Debaryomyces occidentalis. Depending on what milk you use and on the quality of the Kefir grains, Kefir can contain anywhere from 1 billion to 10 billion CFU of bacterial/yeast probiotic per ml (cc). That is 5-50 billion CFU per TSP! It is important to note that Kefir grains, unlike the name suggests, are very much alive, and as such must be taken care of.... As any alive being, it must be fed - but what does it eat? That is the beauty of it: LACTOSE! In kefir, lactic acid bacteria are primarily responsible for the conversion of the lactose present in milk into lactic acid, which results in a pH decrease and milk preservation. Other kefir microbial constituents include lactose-fermenting yeasts that produce ethanol and CO2. Non-lactose fermenting yeast and acetic acid bacteria also participate in the process. After each fermentation "batch", the grains biomass increase in about 5-7%, which is why the bacterial/yeast composition varies according to the milk and process used for fermentation. Unlike the original days, the methods used to produce Kefir at home today differ in several ways. Of course no one is leaving a goat skin bag full of milk by the door to be pounded at, for one! Today Kefir is mostly made in glass jars, kept out of the sunlight to preserve the most amount of vitamins as possible. With that, comes one issue - The grains only feed what they can touch. While some will instruct to pour the milk over the grain in a jar, loosely cover it with a cheese cloth or a plastic lid, put the jar in the cabinet and forget about it for the next 24 hours, I beg it differ. By gently mixing the Kefir every so often you are making sure the grains are evenly distributed, therefore more lactose will be consumed, achieving a more thoroughly fermentation process. This is specially important for cats, which are mostly lactose intolerant. Another way of decreasing the amount of lactose is by doing what is called a "double fermentation" - you simply strain the Kefir after 24 hours into a clean jar, this time closing the lid, and place it into a dark cabinet for another 12-18 hours. The whey will completely separate from the curd, but a smooth texture can be achieved by using a blender. Not only Kefir is virtually lactose free, but studies show that Kefir can actually actually improve lactose digestion and tolerance overtime. The benefits are countless - not only Kefir is a powerful, natural, live probiotic, but it also: In multiple studies, consumption of kefir or kefiran in an animal model has been associated with an increase in microbes thought of as beneficial, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, while simultaneously decreasing harmful microbial species such as Clostridium perfringens (1, 2), Reduces the severity of Giardia , inhibits the adherence of Salmonella typhimurium and E. coli, 1, 2, 3. Kefir has shown a multitude of antibacterial and anti-fungal activities and has been tested in disk diffusion experiments against a wide range of pathogenic bacterial and fungal species, found to have antimicrobial activity equal to ampicillin, azithromycin, ceftriaxone, amoxicillin, and ketoconazole (Cevikbas et al., 1994; Yüksekdağ et al., 2004; Rodrigues et al., 2005; Huseini et al., 2012). Kefir also has anti-inflammatory and healing properties, and was effective in postoperative treatments and in patients with gastrointestinal disorders. Several studies have shown Kefir to have anti-carcinogenic effects 1, 2, 3, and can also act as an anti-oxidant. But one of the major ways probiotic products such as kefir are able to produce health benefits is through the modulation of the gastrointestinal immune system. Kefir has shown in studies anti-allergenic and anti-asthma properties, is capable of decreasing the levels of blood glucose, improving the symptoms of constipation, among many other health benefits. It's important to note that the quality of traditional kefir is mainly influenced by the microorganisms present in kefir grains and kefir processing conditions. Although scientists and food companies attempted to develop a commercial “kefir-type” beverage produced by different cultures and mesophilic and thermophilic lactic acid bacteria, or even pure cultures isolated from kefir grains, their success when compared to traditional kefir is limited. It is suggested that this limitation is due to the microbial diversity present in kefir grains and their interactions, which can determine the probiotic and therapeutic properties of final product, as well as peculiarities conferred by certain minority groups present in different grains. How do you acquire Kefir Grains? Kefir grains are passed on from friends or family, or can also be bought online in sites such as Amazon. When consuming Kefir, you are drinking history! Think about it - you can't just create those grains out of nowhere.... They have been passed around from one person to another, until that they got to you! And the beauty of it? Every time someone used a different milk, a different processing method, temperature, etc - the microbioma in the grain has changed! You will notice that once you start making kefir on a regular basis, your grains will start multiplying exponentially - that's why they are passed around. What else can you do with them? You can eat them - they are just about the most potent probiotic you can get your hands on! Feeding Kefir to your Pets: We cannot stress enough the need to start SLOWLY. And we mean VERY slowly. Kefir is a very potent probiotic, with many substances your pet has never consumed. Dosage: Give a teaspoon to a tablespoon of kefir to small cats or small dogs a day. Medium size dogs – 1 – 2 tbsp. Large dogs – 2 – 3 tbsp. ***Cats specially: Start with 1/8 tsp, and increase every FEW days by doubling the amounts. Give your cat only 1/2 of the dosage for at least one to two weeks before increasing to 3/4 and so on. If your cat has any reactions to Kefir, you can try two things: 1- Do a double fermentation - still reacted? 2- Change the milk for goat milk - still reacted? Stop giving it. I personally had a cat react to kefir, to both Regular Cow's milk and Raw goat milk. I am giving him a break and will try a very slow introduction later on. My other cat seemed to react when I increased the kefir to 1/2 tsp per meal, however the problem was solved with a slower introduction, and a double fermentation. She is also ok with Goat Milk Kefir. I have substituted my cats', mine and my dog's store bought probiotic for Kefir, and everyone is doing terrific! Kefir has been the perfect addition to the kitties' EZComplete diet - how would it not be with so many wonderful properties? YES! Pork is a wonderful meat for cats. Most cats both love pork and do very well with it. At Food Fur Life and in our Raw Feeding for IBD Cats group we often recommend pork loin as a starter meat when introducing raw food to cats. For many it is essentially a “novel” protein. Of course it should be introduced properly and slowly as with any new food or new protein in a raw diet. An excellent source of taurine, pork is a healthy addition to any homemade food protein rotation (though we'd like to note the more electrically active muscles will always have much higher concentrations, e.g. tongue, lung, heart and the dark meats - in pork, being the shoulder). The most maligned meat, many of the myths and misconceptions surrounding the feeding of raw pork are simply outright misinformation; others are outdated health concerns. Let’s address those myths and fears. They are:
Of course, when we say pork is a wonderful raw meat for cats, we do not mean bacon or ham. Salted or smoked meats should never be fed to any pet, due to the sodium content, smoke flavoring chemicals, nitrates and potentially preservatives. But cuts of pork meat: loin, boneless rib meat, butt, shoulder – these are all excellent sources of protein and should be welcomed in any healthy meat rotation in a raw diet. With moderate fat, and low in saturated fats compared to other red meats, pork truly is “the other white meat.” So put your fears aside, and let your kitty enjoy this nutritious protein in its natural state. Let’s face it - very few humans would intentionally choose to eat only dry cereal or only canned stew, even if they were designed to meet all of our daily nutritional requirements. No matter what flavorings were added, most of us would, at some point, crave an apple, a fresh juicy peach or pear, or a cold, crisp salad. Many of us badger ourselves to eat better, and we strive to eat more fresh foods - or at least just not eat as many convenience foods. And if we don’t? Our doctors encourage us to eat more fresh food. We know the more fresh food we include in our diet, the healthier we are, the more energy we have, and the better we feel. We also know that even if we had a power bar for breakfast and fast food for lunch, if we have an apple as a snack, it is better than not eating that apple at all. The same holds true for our cats. Some fresh meat is better than none! Kibble and canned food for cats is convenient. That's what it is for. Our convenience. Just like bagged or canned foods for humans are called "convenience foods." And convenience foods are not the healthiest food choices for us. Just as convenience foods are not the healthiest choices for our cats. But we lead busy lives, and convenience foods make feeding our pets quick and easy; even though it's not what is best for them. And we know this. But when considering a healthier diet for our cats, most of us got – or get – overwhelmed. It is… Too difficult Too time-consuming Too expensive And some of us get to the point of almost hyperventilating by the time we’re wondering things like What meat do I buy? Where do I buy it? How do I store it? Do I need more freezer space? How do I make sure I get it right? Am I going to harm my cat????????? But you know what? It doesn’t have to be all or nothing. At least at first. You don’t have to commit to feeding your cat only homemade food right off the bat. ANY amount of fresh meat you add to your cat's diet is better than none. No need to fret at all. You can start really small. Baby steps! (Even just a slice of apple is better for you than none at all!) If you’re not a vegetarian, and you make meat-based dishes for your family, you’ve already got everything you need to start. Next time you make a meal with meat, just slice off a little bit before you season it. That’s all there is to it to get started! It really IS that simple. You’re holding a tasty, healthy treat for your kitty. When is plain meat is no longer a treat? When the amount you’re giving your cat approaches 10% of the total diet. When it's more than 2 or 3 bits of meat treat a day. Yes, at that point you need to balance that meat to make it a nutritionally complete food. You might want to consider Food Fur Life as a solution for that. EZcomplete fur Cats makes that part quick, easy, and worry-free, allowing you to prepare balanced and complete homemade raw meals in a few simple steps. But please know that even if you’ve moved to balancing the meat, you still don’t have to commit to feeding it full time right away. One meal a week? Two? Three? In fact, we expect that no matter how much you’re able to incorporate, you’ll want to find ways to include more. You’ll see the difference. No matter how little or how much, fresh food will benefit your cat. At that point, feeding more homemade food won't seem so overwhelming. And with the ability to use the supplement with chunks or ground, and to make the food with more water for gravy – or with just a bit of water to make it stick to the meat – your complete and balanced nutritionally complete food made with EZcomplete is actually ideal for snack-style or intermittent feeding. If you’ve been considering ways to improve your kitty’s diet, there’s no reason not to just jump right in. No logistics needed. As Dr. Lisa Pierson’s Andy says on catinfo.org … 
For those concerned about chicken allergies, it's important to note that the body sees chicken muscle meat and egg yolk as two different proteins. A chicken allergy does not mean your kitty is also allergic to egg yolk!
As discussed in our article Hairballs: How Best to Manage Them, often the butt of jokes, hairballs are a sign the stomach of our kitties is not emptying properly. This is a problem with motility, a problem that can lead to or be a symptom of inflammatory bowel disease and/or small cell intestinal cancer. Hairballs are no laughing matter. Proper management of hairballs involves
In that article, we outline why egg yolk and egg yolk lecithin are the first, best methods for managing hairballs in our cats when help is needed. Since writing that article, however, we’ve found that some kitties do not enjoy the additional raw yolk (Please note, food made with EZcomplete fur Cats already contains egg yolk - and most raw or homemade diets also already contain egg yolk, which provides many essential nutrients), and some IBD cats sensitive to fats in the diet cannot tolerate as much egg yolk lecithin as they actually need to resolve hairballs. Food Fur Life co-founder, Carolina, discovered that using powdered egg yolk instead of additional fresh egg yolk made it not only enjoyable for her cats to eat – she no longer needed to give them egg yolk lecithin! (And Carolina has four long-haired rescue kitties, two with IBD). Hairballs, not surprisingly, are a frequent topic of discussion in the Raw Feeding for IBD Cats Facebook group. And we’re finding this approach is helping other cats as well. Group member Eric Swanson decided to make his own homemade powdered, dried egg yolk – and it was both a success and a hit with the cats! How much dried, powdered egg yolk to feed? START SMALL or your cat may experience loose stool or diarrhea. As with all new supplements, it is always best to start with a much smaller amount than you intend to use: make sure your cat does not react to the new addition. Start with a pinch of dried powdered yolk on one meal. Day two, try a big pinch. Day three, use 1/8th teaspoon every-other-day, and work up slowly from there. You can work up to as much as one-quarter yolk a day if needed (in addition to what is provided by the diet), but as always, it is best to use the minimum amount necessary to “get the job done.” Egg yolk in the diet provides many health benefits apart from aiding in hairball management (the egg is a powerhouse of nutrition!) and this amount of egg yolk will not throw the diet out of balance no matter what food you feed. For those with cats with Chronic Kidney Disease, one large egg yolk (which, at 1/4 yolk equivalent a day results in the addition of one yolk every four days) contains the same amount of phosphorus as one ounce of muscle meat. This should not be enough to need to adjust the phosphorus binder you are using if you're using one, but you may want to discuss this with your vet. Recipe / Instructions for Making Homemade Dried, Powdered Egg Yolk Courtesy of Eric Swanson. Photos preparing dried yolk, also thanks to Eric! Use the highest quality eggs you can. Eggs from organically fed, pastured chickens is obviously ideal, but not necessary. 
Eric started with four egg yolks. This recipe works for as many as you care to make.
1) Hard boil the eggs. (Gently lower eggs into boiling water, and boil on medium heat for 12 minutes) 2) When done, run the hard boiled eggs under cold water. 3) When cool, peel the eggshell. (If you make your own eggshell as a calcium source in your cat’s food, save the peeled shells!) 4) Crumble the yolk in a single layer onto a baking pan or into a baking dish. Eric used a Pyrex glass bakeware dish. 
5) Bake at 140F (60C) for 10 hours. If the lowest temperature on your oven is 170F (75C), that's fine, use that and check the yolks after 9 hours to see if they appear to be completely dry. You can stir the yolk after 4 or 5 hours, but it isn't necessary.
6) Remove from the oven (leave it on) and powder the yolk in a food processor or blender. If the yolk is completely dry, you're done! If it feels a tad moist, or a bit "tacky," then 7) Put the now powdered yolk back on the baking sheet / baking dish. 8) Cook the now powdered yolk for up to another two hours so it dries completely. Store in a glass jar in the refrigerator, or a cool, dark place. Four large fresh egg yolks yielded approximately 11.5 teaspoons of powdered yolk (approximately four tablespoons). In this example, one tablespoon of dried yolk powder is the (approximate) equivalent of one large fresh egg yolk. Depending on how fine your processor makes the powder, you may have different results, so it is best you measure the amount of final dried yolk powder to determine how much powder equates to one fresh egg yolk. We recommend feeding up to one-quarter yolk per day, though this amount may not be necessary for all cats. If hairballs do not resolve at that amount, other steps should be taken rather than feeding more powdered egg yolk. You can, of course, purchase commercially prepared powdered, dried egg yolk (not whole egg). Please check for flow agents, many dried powdered egg yolks use them, and it is better to avoid them if possible. Also make sure you know what the fresh yolk equivalent is of the powder you purchase so you can feed the correct amount to your cat, as the fresh yolk equivalent of commercial powders ranges from one teaspoon to one or two tablespoons. Celebrate International Hug Your Cat Day with a Hug for Your Kitty - AND a Hug for Your Pocket!6/4/2016 Celebrate the Power of the Purr! |
Archives
August 2021
Categories
All

|


















 RSS Feed
RSS Feed